Oracle DISTINCT clause is used to remove the duplicate records from the result set. It is only used with SELECT statement.
Syntax:
SELECT DISTINCT expressions
FROM tables
WHERE conditions; Parameters:
expressions:It specifies the columns that you want to retrieve.
tables: It specifies the table from where you want to retrieve records.
conditions: It specifies the conditions that must be fulfilled.
Oracle DISTINCT Example: (with single expression)
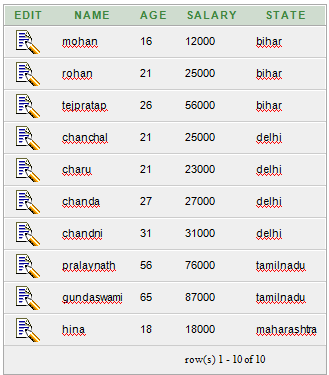
Let’s take a table “customers”
Customer table:
CREATE TABLE "CUSTOMERS"
( "NAME" VARCHAR2(4000),
"AGE" NUMBER,
"SALARY" NUMBER,
"STATE" VARCHAR2(4000)
)
/
Execute this query:
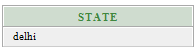
SELECT DISTINCT state
FROM customers
WHERE name = 'charu'; Output:
Oracle DISTINCT Example: (with multiple expressions)
Execute this query:
SELECT DISTINCT name, age, salary
FROM customers
WHERE age >= '60'; Output:
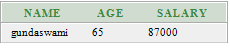
This example specifies distinct name, age and salary of the customer where age is greater than or equal to 65.
Leave a Reply