Introduction to Oracle E-Business Suite
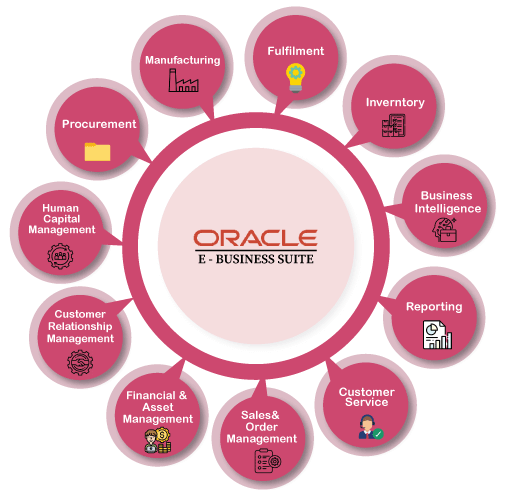
Oracle E-Business Suite, also known as Oracle Applications, is a comprehensive suite of integrated business applications designed to help organizations automate and streamline their business processes. It provides a wide range of modules and functionalities that cover various aspects of enterprise resource planning (ERP), customer relationship management (CRM), supply chain management (SCM), human capital management (HCM), and more.
Oracle EBS offers a robust and scalable solution that caters to the needs of small, medium, and large enterprises across different industries. It is built on a unified data model, allowing seamless integration and information sharing across different modules. This integration enables organizations to achieve better visibility, efficiency, and control over their business operations.
Features of Oracle E-Business Suite
Oracle E-Business Suite (EBS) offers many features and capabilities that help organizations streamline their business processes and enhance operational efficiency. Here are some of the key features of Oracle EBS:
- Comprehensive Suite: Oracle EBS provides a comprehensive suite of integrated business applications covering various functional areas such as finance, supply chain management, human resources, customer relationship management, projects, and more.
- Scalability and Flexibility:
Oracle EBS is designed to scale and adapt to the needs of organizations of all sizes, from small businesses to large enterprises. It offers flexible deployment options, including on-premises and cloud-based deployments, allowing organizations to choose the option that suits their requirements. - Unified Data Model: Oracle EBS is built on a unified data model, which means that data is stored in a consistent and standardized format across different modules. This enables organizations to have a single source of truth and ensures data integrity and accuracy.
- Role-Based Security: Oracle EBS provides robust security features that allow organizations to enforce role-based access control. Users are granted access and privileges based on their roles and responsibilities, ensuring data confidentiality and preventing unauthorized access.
- Workflow Automation: Oracle EBS includes powerful workflow automation capabilities that enable organizations to streamline and automate their business processes.
- Reporting and Analytics: Oracle EBS offers a range of reporting and analytics tools that enable organizations to gain insights into their business performance. It includes standard reports, ad hoc querying, and business intelligence capabilities, allowing users to analyze data and make informed decisions.
- Globalization Support: Oracle EBS is designed to support global operations with multi-currency, multi-language, and multi-country capabilities. It allows organizations to operate in different regions and comply with local regulations and requirements.
- Extensibility and Customization: Oracle EBS provides options for customization and extension to meet unique business needs. It offers development tools, APIs, and frameworks that allow organizations to tailor the system to their specific requirements without compromising the integrity of the core system.
Advantages of Oracle E-Business Suite
Oracle E-Business Suite (EBS) offers several advantages for organizations seeking a robust, integrated business software solution. Here are some of the key advantages of Oracle EBS:
- Comprehensive Functionality: Oracle EBS provides a comprehensive suite of applications that cover various business functions, including finance, supply chain management, human resources, customer relationship management, projects, and more. This eliminates the need for multiple disparate systems and promotes seamless integration across different departments and processes.
- Integrated Business Processes: With its unified data model and integrated modules, Oracle EBS facilitates smooth and consistent data flow across different functions. This integration enables organizations to gain better visibility into their operations, make informed decisions, and optimize processes for improved efficiency and productivity.
- Enhanced Productivity:
Oracle EBS streamlines business processes through workflow automation, reducing manual intervention and improving overall productivity. By automating routine tasks, organizations can free up their employees’ time to focus on more value-added activities, increasing efficiency and productivity. - Data Integrity and Accuracy: With a unified data model and centralized data storage, Oracle EBS ensures data integrity and accuracy across the organization. This helps maintain a single source of truth, eliminate data discrepancies, and provide reliable data for decision-making and reporting.
- Business Intelligence and Analytics:
Oracle EBS offers robust reporting, analytics, and business intelligence capabilities. It provides various tools and options to generate reports, perform ad hoc querying, and gain insights into business performance. This empowers organizations to make data-driven decisions, identify trends, and uncover opportunities for improvement.
- Globalization Support: Oracle EBS is designed to support global operations with features such as multi-currency, multi-language, and multi-country capabilities. It helps organizations comply with local regulations and requirements, manage operations in multiple regions, and handle global supply chains effectively.
Oracle EBS Function
Oracle E-Business Suite (EBS) encompasses a comprehensive set of functions across various modules to support different areas of business operations. Here are some of the key functions provided by Oracle EBS:
Financial Management:
- General Ledger: Manages financial data, chart of accounts, journal entries, and financial reporting.
- Accounts Payable: Handles vendor invoices and payments and manages the accounts payable process.
- Accounts Receivable: Manages customer invoices, receipts and tracks accounts receivable.
- Cash Management: Manages cash flows, bank reconciliation, and cash forecasting.
- Fixed Assets: Tracks and manages fixed assets, depreciation, and asset accounting.
Supply Chain Management:
- Procurement: Handles purchase requisitions, requests for quotations, purchase orders, and supplier management.
- Inventory Management: Manages inventory levels, stock replenishment, item tracking, and cycle counting.
- Order Management: Manages sales orders, order fulfillment, pricing, and shipping processes.
- Logistics: Tracks and manages transportation, shipment, and logistics operations.
Warehouse Management: Controls warehouse activities, including receiving, put-away, picking, and shipping.
Human Capital Management:
- Core HR: Manages employee information, organizational structures, and workforce administration.
- Payroll: Processes payroll, calculates wages, deductions, and manages payroll taxes.
- Benefits: Handles employee benefits programs, enrollment, and benefits administration.
- Performance Management: Supports performance appraisals, goal setting, and performance tracking.
- Talent Management: Facilitates recruitment, onboarding, succession planning, and career development.
Customer Relationship Management:
- Sales Force Automation: Supports sales processes, opportunity management, and sales forecasting.
- Marketing: Manages marketing campaigns, lead generation, and customer segmentation.
- Customer Service: Handles customer inquiries, case management, and service request tracking.
- Contact Center: Manages contact center operations, call routing, and agent productivity.
Projects:
- Project Costing: Tracks project costs, budgets, and expenditures.
- Project Billing: Manages project billing, invoicing, and revenue recognition.
- Resource Management: Handles resource allocation, capacity planning, and project staffing.
- Project Collaboration: Facilitates project collaboration, document sharing, and communication.
Business Intelligence:
- Reporting and Analytics: Provide reporting tools, ad hoc querying, and predefined analytics.
- Dashboards: Displays key performance indicators (KPIs) and real-time data on customizable dashboards.
- Data Warehousing: Supports data consolidation, integration, and storage for business intelligence purposes.
Leave a Reply