The workflow of a Node.js web server typically looks like the following diagram. Let us see the flow of operations in detail:
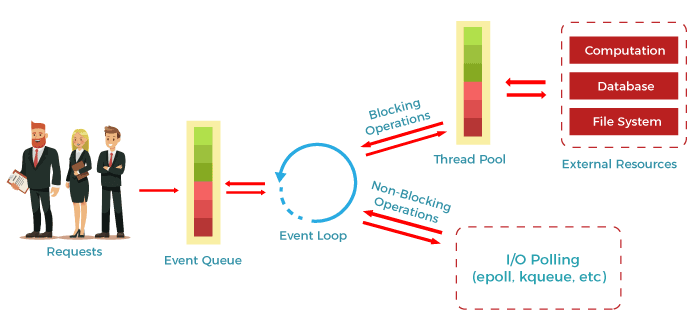
- According to the above diagram, the clients send requests to the webserver to interact with the web application. These requests can be non-blocking or blocking and used for querying the data, deleting data, or updating the data.
- js receives the incoming requests and adds those to the Event Queue.
- After this step, the requests are passed one by one through the Event Loop. It checks if the requests are simple enough not to require any external resources.
- The event loop then processes the simple requests (non-blocking operations), such as I/O Polling, and returns the responses to the corresponding clients.
- A single thread from the Thread Pool is assigned to a single complex request. This thread is responsible for completing a particular blocking request by accessing external resources, such as computation, database, file system, etc.
- Once the task is completed, the response is sent to the Event Loop that sends that response back to the client.
Leave a Reply