- The SQL AND condition is used in SQL query to create two or more conditions to be met.
- It is used in SQL SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE
- Let’s see the syntax for SQL AND:
- SELECT columns FROM tables WHERE condition 1 AND condition 2;
- The SQL AND condition require that both conditions should be met.
- The SQL AND condition also can be used to join multiple tables in a SQL statement.
- To understand this concept practically, let us see some examples.
Consider we have an employee table created into the database with the following data:
| ID | First_Name | Last_Name | Department | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Harshad | Kuwar | Marketing | Pune |
| 2 | Anurag | Rajput | IT | Mumbai |
| 3 | Chaitali | Tarle | IT | Chennai |
| 4 | Pranjal | Patil | IT | Chennai |
| 5 | Suraj | Tripathi | Marketing | Pune |
| 6 | Roshni | Jadhav | Finance | Bangalore |
| 7 | Sandhya | Jain | Finance | Bangalore |
SQL “AND” example with “SELECT” statement
This is how an SQL “AND” condition can be used in the SQL SELECT statement.
Example 1:
Write a query to get the records from emp tables in which department of the employee is IT and location is Chennai.
Query:
mysql> SELECT *FROM emp WHERE Department = "IT" AND Location = "Chennai"; | ID | First_Name | Last_Name | Department | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | Chaitali | Tarle | IT | Chennai |
| 4 | Pranjal | Patil | IT | Chennai |
In the emp table, there are three employees whose department is IT. But we have specified the AND condition according to which the employee’s location should not be other than Chennai. So, there are only two employees whose department is IT and Location is Chennai.
Example 2:
Write a query to get the records from emp tables in which department of the employee is IT and location is Mumbai.
Query:
mysql> SELECT *FROM emp WHERE Department = "IT" AND Location = "Mumbai"; | ID | First_Name | Last_Name | Department | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Anurag | Rajput | IT | Mumbai |
In the emp table, there are three employees whose department is IT. Among these three employees, there is only one employee whose location is Mumbai. Due to the presence of the AND operator used in the query, a record must satisfy both conditions.
SQL “AND” example with “UPDATE” statement
This is how the “AND” condition can be used in the SQL UPDATE statement.
Example 1:
Write a query to update the records in emp tables in which department of the employee is Marketing, and the first name is Suraj. For that particular employee, set the updated value of the location as Delhi.
Query:
mysql> UPDATE emp SET Location = "Delhi" WHERE Department = "Marketing" AND First_Name = "Suraj"; 
We will use the SELECT query to verify the updated record.
mysql> SELECT *FROM emp; | ID | First_Name | Last_Name | Department | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Harshad | Kuwar | Marketing | Pune |
| 2 | Anurag | Rajput | IT | Mumbai |
| 3 | Chaitali | Tarle | IT | Chennai |
| 4 | Pranjal | Patil | IT | Chennai |
| 5 | Suraj | Tripathi | Marketing | Delhi |
| 6 | Roshni | Jadhav | Finance | Bangalore |
| 7 | Sandhya | Jain | Finance | Bangalore |
In the emp table, there are three employees whose department is IT. Among these three employees, there is only one employee whose location is Mumbai. Due to the presence of the AND operator used in the query, a record must satisfy both conditions.
Example 2:
Write a query to update the records in the emp table in which department of the employee is Finance and ID is 7. For that particular employee, set the updated value of the department as HR.
Query:
mysql> UPDATE emp SET Department = "HR" WHERE Department = "Finance" AND ID = 7; 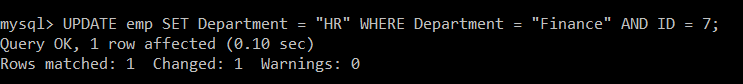
We will use the SELECT query to verify the updated record.
mysql> SELECT *FROM emp; | ID | First_Name | Last_Name | Department | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Harshad | Kuwar | Marketing | Pune |
| 2 | Anurag | Rajput | IT | Mumbai |
| 3 | Chaitali | Tarle | IT | Chennai |
| 4 | Pranjal | Patil | IT | Chennai |
| 5 | Suraj | Tripathi | Marketing | Delhi |
| 6 | Roshni | Jadhav | Finance | Bangalore |
| 7 | Sandhya | Jain | HR | Bangalore |
In the emp table, there are two employees whose department is Finance. Among these two employees, there is only one employee whose ID is 7. Due to the presence of AND operator used in the query, a record must have the department as Finance and ID as 7.
SQL “AND” example with “DELETE” statement
This is how an SQL “AND” condition can be used in the SQL DELETE statement.
Example 1:
Write a query to delete the records from the emp table in which the last name of the employee is Jain, and the Location is Bangalore.
Query:
mysql> DELETE FROM emp WHERE Last_Name = 'Jain' AND Location = 'Bangalore'; 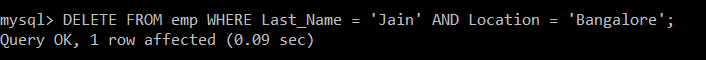
We will use the SELECT query to verify the deleted record.
mysql> SELECT *FROM emp; | ID | First_Name | Last_Name | Department | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Harshad | Kuwar | Marketing | Pune |
| 2 | Anurag | Rajput | IT | Mumbai |
| 3 | Chaitali | Tarle | IT | Chennai |
| 4 | Pranjal | Patil | IT | Chennai |
| 5 | Suraj | Tripathi | Marketing | Delhi |
| 6 | Roshni | Jadhav | Finance | Bangalore |
There is only one record in the emp table whose last name is Jain. But still, due to the presence of AND operator, the second condition will also be checked according to which employee’s location should be Bangalore. So, only that particular record is deleted.
Example 2:
Write a query to delete the records from the emp table in which department of the employee is IT and Location is Mumbai.
Query:
mysql> DELETE FROM emp WHERE Department = 'IT' AND Location = 'Mumbai'; 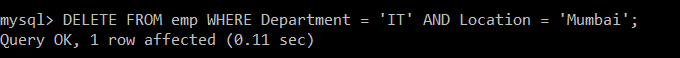
We will use the SELECT query to verify the deleted record.
mysql> SELECT *FROM emp; | ID | First_Name | Last_Name | Department | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Harshad | Kuwar | Marketing | Pune |
| 3 | Chaitali | Tarle | IT | Chennai |
| 4 | Pranjal | Patil | IT | Chennai |
| 5 | Suraj | Tripathi | Marketing | Delhi |
| 6 | Roshni | Jadhav | Finance | Bangalore |
There are three records in the emp table whose department is IT. But only one record is deleted from the emp table, which contains a total of 6 records. This happened because of the AND operator according to which the employee’s location should mandatorily be Mumbai. Therefore there is only one record that satisfies both the conditions. Hence, it is deleted.
Leave a Reply