This statement specifies that Oracle will fire this trigger AFTER the INSERT/UPDATE or DELETE operation is executed.
Syntax
CREATE [ OR REPLACE ] TRIGGER trigger_name
AFTER INSERT or UPDATE or DELETE
ON table_name
[ FOR EACH ROW ]
DECLARE
-- variable declarations
BEGIN
-- trigger code
EXCEPTION
WHEN ...
-- exception handling
END; Parameters
OR REPLACE: It is an optional parameter. It is used to re-create the trigger if it already exists. It facilitates you to change the trigger definition without using a DROP TRIGGER statement.
trigger_name: It specifies the name of the trigger that you want to create.
AFTER INSERT or UPDATE or DELETE: It specifies that the trigger will be fired after the INSERT or UPDATE or DELETE operation is executed.
table_name: It specifies the name of the table on which trigger operation is being performed.
Limitations
- AFTER trigger cannot be created on a view.
- You cannot update the OLD values.
- You can only update the NEW values.
Oracle AFTER Trigger Example
Consider, you have a “suppliers” table with the following parameters.
CREATE TABLE "SUPPLIERS"
( "SUPPLIER_ID" NUMBER,
"SUPPLIER_NAME" VARCHAR2(4000),
"SUPPLIER_ADDRESS" VARCHAR2(4000)
)
/ You can use the following CREATE TRIGGER query to create a AFTER INSERT or UPDATE or DELETE Trigger:
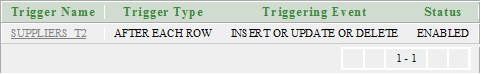
CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER "SUPPLIERS_T2"
AFTER
insert or update or delete on "SUPPLIERS"
for each row
begin
when the person performs insert/update/delete operations into the table.
end;
/
ALTER TRIGGER "SUPPLIERS_T2" ENABLE
/ Here the trigger name is “SUPPLIERS_T2” and it is fired AFTER the insert or update or delete operation is executed on the table “suppliers”.
Leave a Reply