FROM clause is a mandatory clause in SELECT expression. It specifies the tables from which data is to be retrieved.
Syntax:
FROM table_name...
Expressions...Oracle FROM Clause Example: (with one table)
Let’s take an example to explain how to use FROM clause to retrieve data from one table. Consider a table “customers”.
Customer table:
CREATE TABLE "CUSTOMERS"
( "NAME" VARCHAR2(4000),
"AGE" NUMBER,
"SALARY" NUMBER,
"STATE" VARCHAR2(4000)
)
/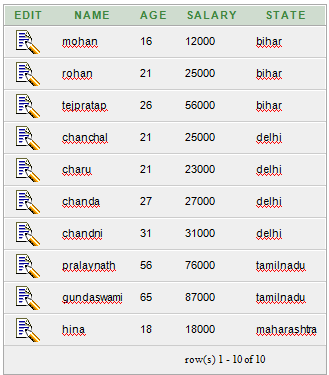
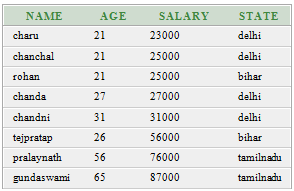
Execute this query:
SELECT *
FROM customers
WHERE salary >= 20000
ORDER BY salary ASC; Output:
Oracle FROM Clause Example: (with two tables)
Inner Join example:
Let’s take two tables “suppliers” and “order1”.
Suppliers:
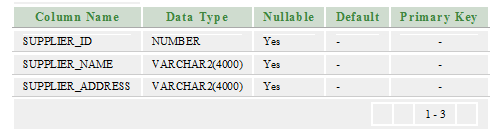
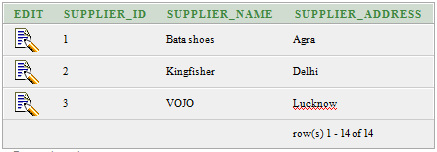
Order1:
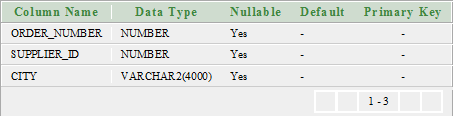
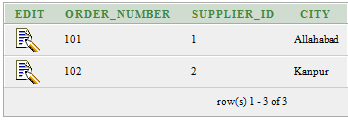
Execute the following query:
SELECT suppliers.supplier_id, suppliers.supplier_name, order1.order_number
FROM suppliers
INNER JOIN order1
ON suppliers.supplier_id = order1.supplier_id;Output:

Leave a Reply