In Oracle, ORDER BY Clause is used to sort or re-arrange the records in the result set. The ORDER BY clause is only used with SELECT statement.
Syntax:
SELECT expressions
FROM tables
WHERE conditions
ORDER BY expression [ ASC | DESC ]; Parameters:
expressions: It specifies columns that you want to retrieve.
tables: It specifies the table name from where you want to retrieve records.
conditions: It specifies the conditions that must be fulfilled for the records to be selected.
ASC: It is an optional parameter that is used to sort records in ascending order.
DESC: It is also an optional parameter that is used to sort records in descending order.
Oracle ORDER BY Example: (without ASC/DESC attribute)
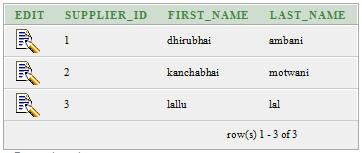
Let’s take a table “supplier”
Supplier table:
CREATE TABLE "SUPPLIER"
( "SUPPLIER_ID" NUMBER,
"FIRST_NAME" VARCHAR2(4000),
"LAST_NAME" VARCHAR2(4000)
)
/
Execute this Query:
SELECT *
FROM supplier
ORDER BY last_name; Output:
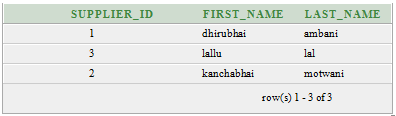
The above example returns the first_name ordered by last_name in ascending order.
Oracle ORDER BY Example: (sorting in descending order)
If you want to sort your result in descending order, you should use the DESC attribute in your ORDER BY clause:
Execute this Query:
SELECT *
FROM supplier
ORDER BY last_name DESC;Output
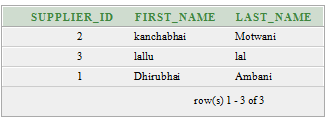
The above example returns the first_name ordered by last_name in descending order.
Leave a Reply